Consumers Spending Less on Electronics, Impact on Apple, Swiss Watch Sales Data for 2022 (Daily Update)
Hello everyone. Happy Wednesday. It feels good to get back into the swing of things after a little time off.
We kick off today’s update with Neil’s thoughts on Walmart and Home Depot pointing to major shifts in how consumers are spending their money. We look specifically at the impact the trend will have on Apple. The update concludes with an examination of Swiss watch industry sales for 2022 and why Neil thinks Apple Watch continues to impact the Swiss.
Consumers Spending Less on Electronics
Earlier today, a WSJ article with the headline “Walmart, Home Depot Give Cautious Outlook as Shoppers Spend More on Basics,” jumped out at me. Here’s Sarah Nassauer:
“Consumers are spending more on food and less on electronics, apparel and home improvements as inflation and changing habits zap demand for many goods, two of the country’s largest retailers reported Tuesday.
Walmart Inc. and Home Depot Inc. have enjoyed robust sales for much of the past two years as people looked for bargains or fixed up their homes. Now more of shoppers’ budgets are going to higher-priced groceries and travel, executives said.
For Home Depot, which primarily sells home-improvement goods, that dynamic meant flat sales in the most recent quarter. For Walmart, which relies on groceries for the majority of its sales, it meant larger-than-expected sales growth. But executives from both companies said consumers’ spending habits pressured profits and they gave muted outlooks for the rest of the year amid economic uncertainty.
‘Customers are still spending money,’ said Walmart Chief Executive Doug McMillon. ‘It’s obviously not as clear to us what the back half of the year looks like.’”
The following slide from Walmart’s earnings release serves as a helpful summary of what the largest retailer is seeing:
An Above Avalon membership is required to continue reading this update. Members can read the full update here. An audio version of this update is available to members who have the podcast add-on attached to their membership. More information about the podcast add-on is found here.
(Members: Daily Updates are always accessible by logging into Slack. If you haven’t logged into Slack before, fill out this form to receive an invite.)
Above Avalon Membership
Payment is processed and secured by Stripe. Apple Pay and other mobile payment options are accepted. Special Inside Orchard bundle pricing is available for Above Avalon members.
More information about Above Avalon membership, including the full list of benefits and privileges, is available here.
Measuring Apple Watch’s Sales Potential, Apple Contemplating Apple TV Ad Play, ByteDance Planning Spotify Battle (Daily Update)
Hello everyone. We will kick off today's update with one follow-up to yesterday's Apple Watch discussion.
Measuring Apple Watch’s Sales Potential
Yesterday, we talked about Apple Watch sales and adoption trends up to the end of September 2022.
As for looking forward, there is no near-term ceiling as to the percent of iPhone users who will embrace Apple Watch. The Apple Watch ushered in a paradigm shift in computing, even if consensus still isn't willing to acknowledge the shift. Since wearables are capable of making technology more personal, there will be a natural evolution involving consumers gradually finding spots in their lives for wearables.
An Above Avalon membership is required to continue reading this update. Members can read the full update here. An audio version of this update is available to members who have the podcast add-on attached to their membership. More information about the podcast add-on is found here.
(Members: Daily Updates are always accessible by logging into Slack. If you haven’t logged into Slack before, fill out this form to receive an invite.)
Above Avalon Membership
Payment is processed and secured by Stripe. Apple Pay and other mobile payment options are accepted. Special Inside Orchard bundle pricing is available for Above Avalon members.
The daily updates have become widely read and influential in the world of Apple and technology. They are unmatched in the marketplace in terms of comprehensive analysis and research on all things Apple. Members reside in 60 countries and hold a diverse range of backgrounds and occupations. They include Silicon Valley executives and investors, the largest Apple shareholders, and the leading Apple journalists in the business.
More information about Above Avalon membership, including the full list of benefits and privileges, is available here.
Apple Has a Decade-Long Lead in Wearables
Last week, Apple quietly unveiled one of the more remarkable pieces of technology that has been developed in the past few years. AssistiveTouch allows one to control an Apple Watch without actually touching the device. Instead, a series of hand and finger gestures can be used to control everything from answering a call to ending a workout. The video below showcasing AssistiveTouch is quite impressive:
Just two months prior, Facebook went on a big PR push to show the world how it was in early R&D stages of working on technology that can also use hand and finger movements to control future gadgets. AssistiveTouch is just the latest example of how Apple’s lead in wearables is still being underestimated. The evidence points to Apple having a wearables lead of not just a few years but more like a decade.
Apple Wearables by the Numbers
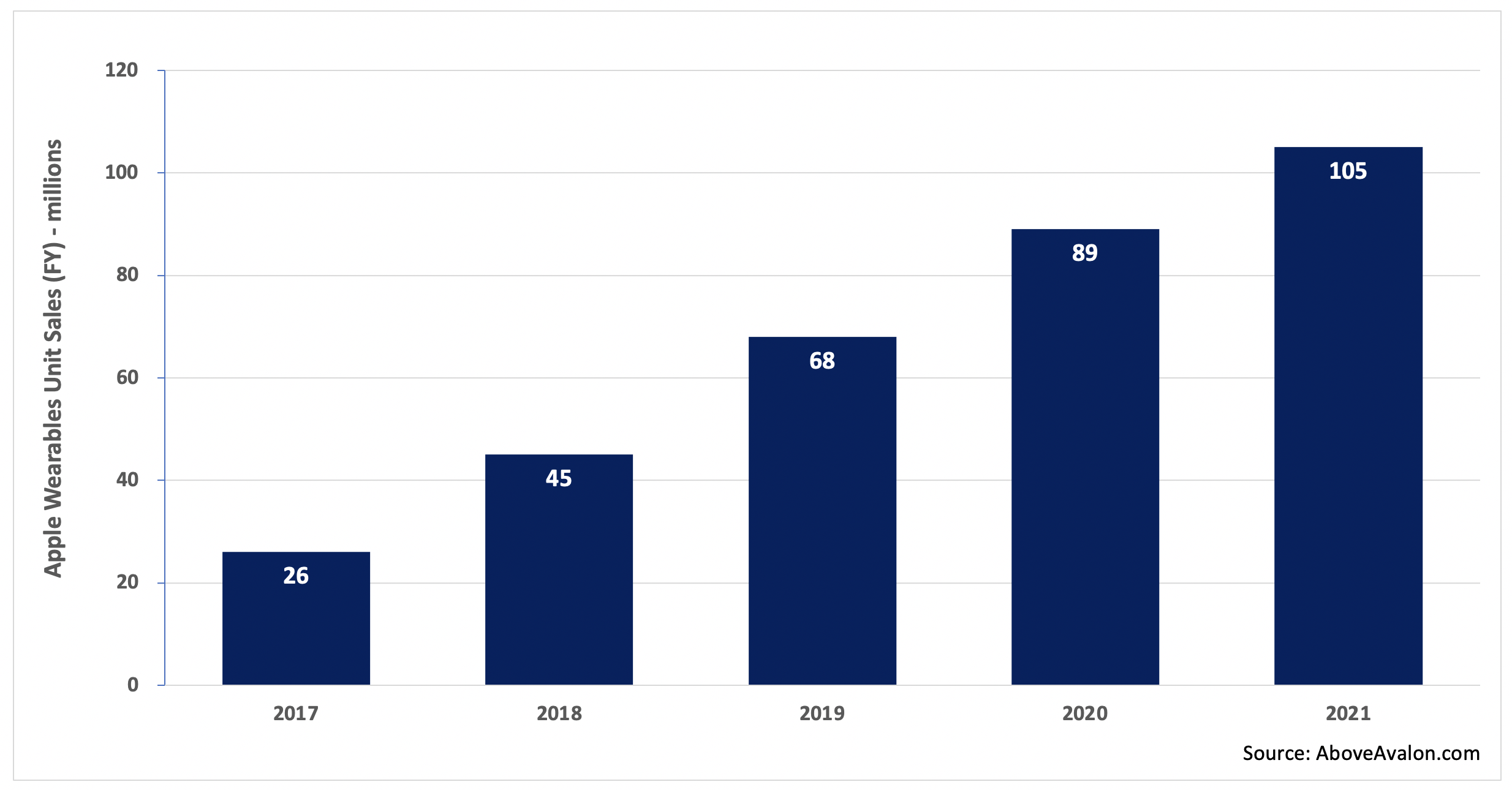
According to my estimate, Apple is on track to sell more than 100 million wearable devices in 2021. That total represents nearly 40% of the number of iPhones that will be sold during the same time period. Unit sales don’t tell the full story, however. On a new-user basis, Apple is seeing more people enter the wearables arena than buy a new iPhone for the first time.
Exhibit 1: Apple Wearables Unit Sales (2017 to 2021)
Note: Apple wearables include Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
On a revenue basis, Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones are a $30 billion per year business. That would rank Apple wearables on a combined basis just shy of a Fortune 100 company. Assuming continued Apple Watch and AirPods momentum, along with Apple expanding its wearables platform by getting into face wearables (AR/VR headsets and glasses), Apple wearables will likely be able to generate up to $50 billion of revenue annually within a few years.
Exhibit 2: Apple Wearables Revenue (2017 to 2021)
Note: Apple wearables include Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
Measuring Apple’s Lead
When Apple unveiled the iPhone in January 2007, Steve Jobs famously said that the iPhone was “literally five years ahead of any other mobile phone.” He ended up being mostly correct. It took the competition a number of years, and a whole lot of copying, to catch up with what Apple had just unveiled.
With wearables, my suspicion is Apple’s lead is longer than five years. There are three components to Apple’s wearables lead:
Custom silicon / technology / sensors (a four to five-year lead over the competition, and that is being generous to the competition)
Design-led product development processes that emphasizes the user experience (adds three years to Apple’s lead)
A broader ecosystem build-out in terms of a suite of wearables and services (adds two years to Apple’s lead)
Apple has at least a four-to-five year lead over the competition when thinking about just the technology powering its wearables. Everything from custom silicon and health monitoring sensors to audio and AR-focused technologies come together to set Apple apart from the competition. Only a select number of companies will likely be able to even compete with Apple on the technology front. Others will be forced to pursue partnerships.
Apple’s wearables lead extends beyond four to five years when taking into account attributes that set wearables apart from mobile devices. Succeeding on the technology front is not enough. Wearables need to be designed so that people want to be seen wearing them for extended periods of time. A smartwatch or wireless pair of headphones must also be able to work seamlessly with other devices and services. A competitor needs to have not only an answer for effectively competing with Apple Watch on the wearables front, but also answers for various services available on AirPods and Apple’s other devices. Looking ahead, Apple’s entry into face wearables will only make the hill to climb that much steeper for competitors trying to go after Apple Watch and AirPods.
For competitors, the intimidating part is that the pieces needed to compete effectively with Apple wearables are unable to be worked on concurrently (at the same time). A company needs to first spend the required years developing and researching the core technologies before turning its focus on ensuring the right kind of collaboration exists between engineering and design. Product sales will then need to materialize before a company has the means of leaning on an ecosystem to sell additional wearable devices.
Apple M&A
A different way of measuring Apple’s lead in wearables is to look at the company’s M&A activity. Apple has been busy buying tech and talent for its upcoming face wearables play for the past six years. In wearables land, the days of new products taking only two to three years to develop are over. The required technology and R&D required to get such devices off the ground require much more lead time.
Metaio - AR (2015)
SensoMotoric Instruments – AR glasses (2017)
Vrvana – AR / hand & positional tracking technology (2017)
Akonia Holographics – AR glasses (2018)
NextVR – content platform for wearables (2020)
Spaces – content platform for wearables (2020)
Examples of Apple’s Lead
There are a number of real-world examples demonstrating Apple’s significant lead in wearables.
AssistiveTouch vs. Facebook Reality Labs. Two months ago, Facebook gave the press a peek at how it is researching using a smartwatch-like device as an input method for a pair of AR glasses. The research, centered on electromyography, looked to be in the pretty early stages with many years needed before seeing the technology in a consumer-facing product. The video was intriguing as it showed research that was thought to be at the forefront of what is going on in technology R&D today. Apple then shocked everyone by unveiling AssistiveTouch for Apple Watch. Instead of showing a behind-the-scenes look at an R&D project, Apple unveiled a technology ready for users today. The technology, relying on a combination of sensors and technologies to turn the Apple Watch into a hand / finger gesture reader, was designed for those in need of additional accessibility. Of course, the technology can go on to have other use cases over time, such as controlling a pair of smart glasses like the ones Facebook is working on. AssistiveTouch does a good job of showing just how far ahead Apple is on the wearables R&D front.
Google I/O 2021. At its 2021 developers conference, Google showed signs of finally taking wrist wearables seriously by ditching Wear OS and partnering with Samsung on a new OS. While it is fair to be skeptical that the effort will end up being successful, the announcement was a marked change from prior Google I/Os when wearables were all but ignored. Diving a bit deeper into Google’s announcement, it’s easy to see how far behind Google truly is in wearables. The company doesn’t even have an OS capable of powering a smartwatch. This may be excusable if Apple Watch was just unveiled. However, last month marked Apple Watch’s sixth anniversary.
Snap Spectacles 4 / Microsoft HoloLens / Magic Leap. While we see a handful of companies release various kinds of prototype hardware for the face (AR/VR/mixed reality), nothing has stuck with consumers. The feeling in the air is that they all lack something – design thinking. This is an item that is not easy to recreate with most companies simply not structured to emphasis design. Many companies will need to rethink their face wearables strategies once Apple enters the market. None have viable answers for smartwatches or wireless headphones either, which make their face-focused efforts look incomplete.
How Did This Happen?
Apple’s lead in wearables wasn’t driven by any one factor or item. Instead, a series of events came together to give Apple an advantage.
Apple was early. One way to build a big lead against the competition is to get an early start. Wearables represent a paradigm shift in computing, and few companies other than Apple saw it coming. As for how Apple was able to see it so early, wearables are all about making technology more personal - a mission Apple has been on for decades. In a way, Apple was built to excel with wearables. Apple’s lack of fear in coming up with new products that may potentially impact sales of existing products also helped the company run wrist-first into wearables in the early 2010s.
Voice computing distraction. Even after Apple began to unveil its wearables strategy, many competitors balked at following the company. Competitors thought the actual paradigm shift materializing was found with voice computing. Most of these companies didn’t have the hardware expertise to do well with wearables out of the gate, so they pinned their hopes on voice assistants being piped through stationary speakers. Once the stationary smart speaker mirage became apparent, companies found themselves years behind Apple on the wearables front.
Wearables require design expertise. It’s not enough to just throw together some leftover smartphone components and ship wearables. People want to wear devices that they are OK with being seen in. This is one reason why so many companies have looked at Apple Watch for design cues. The lack of design talent and ability remains a major roadblock for many companies.
Ecosystem and technology advantage. Wearables are the ultimate ecosystem play. On the technology front, Apple was able to utilize lessons learned from mobile devices to push wearables forward. Not many companies are able to do the same. Consolidation in the smartphone space has left only a handful of companies even in a position to have a wearables and mobile ecosystem. The probability of there being a wave of smartwatch OEMs utilizing something akin to Android remains low.
No price and feature umbrellas under Apple. One reason Android found oxygen in the smartphone space is that Apple left a pretty wide price umbrella under the iPhone. In addition, Android positioned itself as giving users features that iPhone users may not have had access to. No such umbrellas exist in wearables. Entry-level AirPods sell for $159 and are often available for less at third-party retailers. Apple Watch is available starting at $199. It is very difficult for a hardware manufacturer to sell wearables for less than Apple and turn a profit. Meanwhile, companies that would look to make money in other ways, such as through data collection, are still stuck with the requirement of wearables needing to look good enough to be worn in public.
Six years after releasing the Apple Watch, it’s still not clear who is going to represent genuine competition for Apple in the wearables space. Apple’s success in wearables is finally being noticed by others, as seen by the growing number of companies selling products for the body (Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, Google, Samsung, Huawei, Xiaomi, Garmin, and the list goes on). However, none are in as strong of a position as Apple was in a few years ago, let alone today. Apple’s wearables lead stands to grow further once the company enters face wearables. The next few years will likely dictate the power structure in wearables for the next 10 to 20 years. When it comes to competitors figuring out a way to slow Apple in wearables, it’s now or never.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (3 stories per day, 12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Above Avalon Podcast Episode 163: A Revolution on the Wrist
In addition to being a sales success, the Apple Watch has ushered in a paradigm shift in computing. In episode 163, Neil discusses how the Apple Watch is fundamentally changing the way we use technology. Additional topics include paradigm shifts, Apple Watch sales, Apple’s new Apple Watch Connected initiative, stationary smart speakers as extensions of existing products, and Neil’s new framework for recognizing paradigm shifts in computing.
To listen to episode 163, go here.
The complete Above Avalon podcast episode archive is available here.
Apple Watch and a Paradigm Shift in Computing
Despite being only four years old, the Apple Watch has fundamentally changed the way we use technology. Due to the sheer number of Apple Watches now seen in the wild, those claiming the device is unpopular have been silenced. However, there continues to be a good amount of cynicism thrown at the computer found on 65 million wrists around the world.
Many tech analysts and pundits continue to look at the Apple Watch as nothing more than an iPhone accessory - an extension to the smartphone that will never have the means or capability of being revolutionary. Such a view is misplaced as it ignores how the Apple Watch has already ushered in a paradigm shift in computing.
Paradigm Shifts
The idea of paradigm shifts was born in the sciences to describe a scenario requiring a new way of thinking in order to explain the world. One of the more fascinating aspects of paradigm shifts is the accompanying social component. Due to the discomfort found with letting go of legacy thinking, society has a built-in aversion to acknowledging when a paradigm shift has occurred due to the discomfort found with letting go of legacy thinking. This makes it likely that paradigm shifts will often be born wrapped in skepticism and doubt.
In terms of computing, no one now questions the shift that took place from desktops and laptops to mobile devices. However, reality was messier as it took nearly a decade for consensus to view the smartphone as a laptop or desktop alternative. For years, smartphones were viewed as merely laptop and desktop extensions. What was initially viewed as a superior email machine for executives marked the start of a paradigm shift in the making.
We are seeing a similar dynamic take place with Apple Watch. Legacy thinking is masking Apple Watch’s transformational attributes. The product is misunderstood as Apple competitors are unsure of the answers to basic questions such as, why are consumers buying Apple Watches?
A Wrist Revolution
While pundits and analysts question what an Apple Watch is for, tens of millions of consumers around the world have recognized how the device can improve their lives. The product category is a sales success.
Apple has sold more than 90 million Apple Watches to date with 29 million sold in calendar year 2019. With an average selling price of more than $400, the Apple Watch is bringing in $12 billion of revenue per year, and that total is growing by 30% per year. After taking into account upgrade trends, the number of people wearing an Apple Watch has crossed 65 million. Based on my forward projections, the Apple Watch installed base will surpass 100 million people in 2021.
The preceding numbers are my estimates obtained by utilizing more than four years of financial clues and insights provided by Apple management in earnings calls, interviews, and presentations. More information on my methodology and the math behind these numbers is found in the Above Avalon daily update from December 11th. Above Avalon membership is required to read my daily updates.
Apple Watch and Paradigm Shifts
In addition to being a sales success, the Apple Watch has ushered in a paradigm shift in computing by making technology more personal in a way that other devices have failed to accomplish or replicate. The Apple Watch allows people to get more out of technology without having technology take over people’s lives. The device is able to accomplish this in three ways:
Seamless tracking and monitoring. The Apple Watch tracks one’s fitness and more importantly, health, in a nonintrusive and intuitive way that isn’t possible with non-wearable devices.
Intelligent assisting. Wearing a computer on the wrist has shown the value found in having a digital assistant push small amounts of information and data to the user throughout the day instead of having the user pull data from pieces of glass (smartphones and tablets).
Contextual awareness. A device that is always on us can enhance our surroundings by utilizing our location and activity to deliver contextual experiences. This is a valuable proposition when developing new experiences.
These three items combined allow Apple Watch to handle some tasks that we already give to existing devices like smartphones and tablets as well as jobs and work that cannot be supported by mobile devices.
Apple Watch Connected
Apple Watch’s ability to usher in a paradigm shift in computing isn’t about what ifs or hypotheticals. It's something that is already taking place. We have a growing list of ways Apple Watch is a different kind of computer, the likes of which we have never seen. The latest example is an initiative Apple soft launched two weeks ago with four fitness brands called Apple Watch Connected.
The initiative originated out of feedback shared with Apple from health and fitness clubs looking to better connect the Apple Watch with their own customer experiences.
There are four requirements for a health club or gym to be part of Apple Watch Connected (which is free for both the health club and Apple Watch wearer):
Support Apple Pay. Apple Watch wearers must be able to purchase items like water, classes, or even personal training on the wrist with Apple Pay.
iOS and watchOS Apps. Businesses must have apps that allow for things like signing up for classes.
Earn with Watch. Businesses must offer rewards and incentives to Apple Watch wearers for remaining active. Such incentives have proven to be an effective way to motivate Apple Watch wearers.
Support GymKit (if applicable).
Apple Watch Connected ends up being a tool that enables third-party gyms and health clubs to build stronger relationships with customers. This is accomplished when businesses leverage seamless activity and fitness tracking on the wrist to reward their customers for staying active.
The key ingredient for getting this initiative off the ground is having people wear an Apple Watch throughout the day. Trying to recreate this type of comprehensive experience on a dedicated fitness tracker used only during workouts, or even on a smartphone or tablet, would be the equivalent of trying to use a laptop or desktop to accomplish tasks that are simpler and more intuitive on an iPhone. There is no good or easy way to track our daily activity with a large piece of glass that may sometimes be in our pocket or strapped to our arm. Having to grab and hold this piece of glass when using mobile payments or checking location-based notifications and reminders would lead to an overall experience that is subpar.
The most intriguing aspect of Apple Watch Connected is how entrepreneurs can use Apple Watches to launch new business models. With legacy gyms, the idea was to have people pay for monthly memberships but then not show up so that fewer workout machines would be needed. Apple Watch Connected turns that idea on its head by allowing a gym or health club to establish a new kind of long-term relationship with customers that encourages continued workouts and activity. This kind of business model shift is an example of the new paradigm shift unleashed by Apple Watch.
Instead of simply taking the existing app model and applying it to the wrist, a new way of consuming “apps” has developed. Subscriptions are naturally more applicable to something like an Apple Watch as customers find value in long-term targeting, monitoring, and data curation.
A New Framework
I’m introducing a new framework for recognizing paradigm shifts in computing. This theory borrows heavily from my Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products which positions a product category's design as tied to the role it is meant to play relative to other Apple products.
More information on the Grand Unified Theory is found in the Above Avalon Report Product Vision: How Apple Thinks About the World. Reports are available to Above Avalon members at no additional cost.
Paradigm shifts in computing can be determined by monitoring the degree to which products are able to make technology more personal. This framework positions design (i.e. how we use products) as the catalyst for paradigm shifts in computing.
Over the past few decades, we have seen two such primary paradigm shifts in computing:
Laptops/desktops to smartphones.
Smartphones to wearables.
Neither shift was about a new product replacing an older product. Laptops and desktops are still used by hundreds of millions of people in a mobile world. Similarly, there will be billions of smartphones found in a wearables world.
Instead, the move from desktops and laptops to smartphones and tablets was ultimately about using design to remove barriers that existed between the user and technology. One way this was accomplished was using multitouch as a new way to interact with a device. However, mobile devices are not able to remove all barriers. Increased smartphone and tablet usage has revealed an entirely new set of barriers that we never knew existed. A device like Apple Watch relies on design to remove some of those recently discovered barriers.
One reason this new computing shift has not been universally accepted is because the Apple Watch still uses “training wheels” in the form of requiring an iPhone to set up. This iPhone reliance has led some to view Apple Watch as nothing more than an extension to the iPhone. However, such a claim focuses too much on the technology and not enough on how design is leveraged to alter the way we use technology.
As for an example of a genuine extension of the smartphone, stationary smart speakers are at the top of the list. Grand prognostications of stationary smart speakers ushering in a new era of computing have faded (which doesn't come as a surprise). The primary value found with a stationary smart speaker is being able to take up the physical space needed to house speakers for delivering better sound. In this way, the speaker ends up being a smartphone amplifier that comes in handy for consuming sound as a group activity.
Nearly every other task or role given to a stationary smart speaker could be given to an Apple Watch. The wrist ends up being a better solution given the presence of a screen. In addition, whereas stationary speakers are confined to a finite area (the inside of a room), Apple Watch has greater mobility than even smartphones and tablets as it is literally strapped to our wrist at all times.
Voice in and of itself is not a paradigm shift as the medium is incredibly inefficient for transferring large amounts of data and information. It also creates a massive wall that prevents us from getting more out of technology without having technology take over our lives. Meanwhile, the Apple Watch has become a bridge to the future by containing a screen.
Apple Watch in a Wearables World
Apple Watch isn’t alone in ushering in this new era of computing. Other wearable devices designed to leverage the unique attributes of the body (wrists, ears, and eyes) have a role to play. The attributes that have allowed the Apple Watch to flourish on the wrist are being translated to allow AirPods to become a platform for bringing augmented hearing to the masses. In the future, a pair of eyeglasses will be able to add visual context to our surroundings.
In each example, we have a fundamental rethink of how people use computers to improve their lives. The “training wheels,” or early technological bonds that may exist in the early reiterations of these devices should not be taken or viewed as permanent chains. Rather, they are early support systems designed to give wearables the power to change the way we use technology.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
For additional discussion on this article, check out the daily update from February 6th: A Paradigm Shift on the Wrist. The update goes over an example of how the Apple Watch isn't just addressing tech barriers that have been around for years, but also newer barriers that only recently became visible.